Introduction
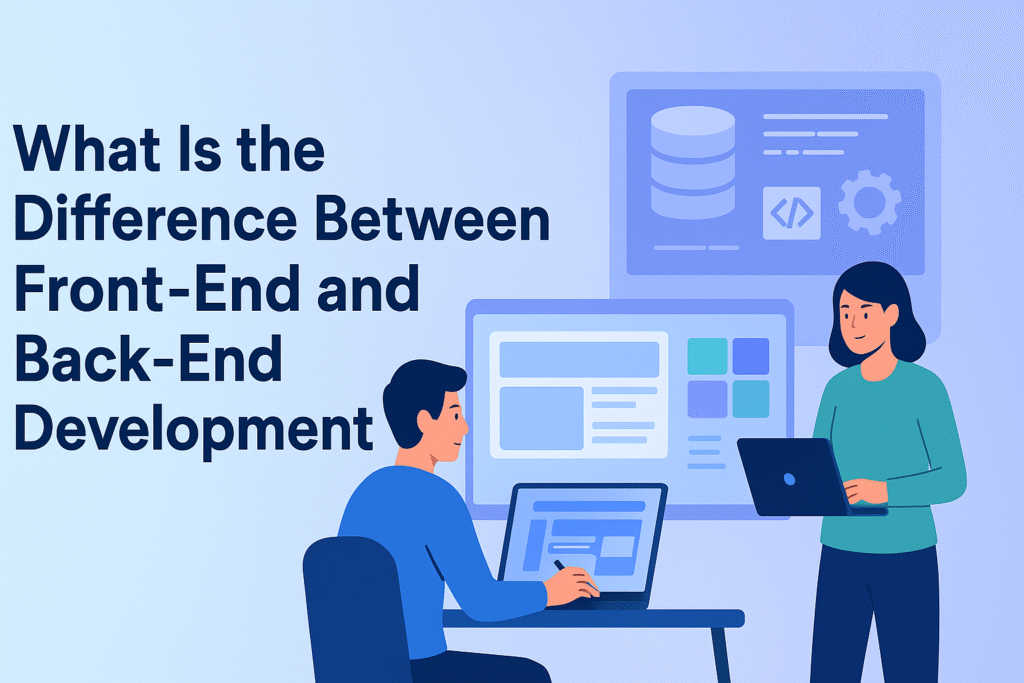
In today’s digital-first world, websites and applications have become an integral part of our daily lives. Whether you’re scrolling through social media, shopping online, or using a business portal, every digital interaction is powered by two essential pillars of web development: the front-end and the back-end.
The front-end is everything you see, the design, buttons, colors, and layouts—crafted to deliver a smooth user experience. The back-end, on the other hand, is what you don’t see. It works behind the scenes, handling data, server requests, and application logic to make sure everything functions correctly.
Understanding the difference between front-end and back-end development is more than just tech jargon—it’s about recognizing how these two disciplines come together to create seamless digital products. For aspiring developers, this knowledge helps in choosing a career path. For businesses, it provides clarity on hiring the right expertise. And for curious learners, it’s the foundation of knowing how the internet really works.
What Is Front-End Development?
The front-end of a website or application is the part that users directly see and interact with. Every visual element—from navigation menus and search bars to forms, images, and colors—belongs to the front-end. Its main purpose is to create an attractive, intuitive, and user-friendly interface that ensures visitors can easily navigate the site and enjoy their experience.
Front-end developers are often referred to as the “architects of the user experience.” They transform design mockups or wireframes into real, functional interfaces. A well-built front-end makes the difference between a frustrating website and one that keeps users engaged and coming back.

Popular Front-End Technologies
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) – Defines the structure of content, such as headings, paragraphs, and images. Without it, a page wouldn’t have any layout.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) – Handles styling, colors, fonts, and positioning. CSS makes websites visually appealing and ensures they look consistent across devices.
- JavaScript – Adds interactivity. From live form validation and dropdown menus to animations and sliders, JavaScript turns static designs into dynamic experiences.
- Frameworks and Libraries – React, Angular, and Vue.js help speed up development and make it easier to build modern, feature-rich applications.
👉 A front-end developer’s role doesn’t stop at coding. They must also consider responsiveness (so sites look good on phones, tablets, and desktops) and accessibility (ensuring all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate easily).
What Is Back-End Development?
If the front-end is the “storefront” of a business, the back-end is the warehouse, inventory system, and employees who keep everything running smoothly behind the scenes. It powers the website by storing, processing, and securing data.
Back-end developers build and maintain the invisible systems that handle everything from account logins and product orders to data storage and payment gateways. Without the back-end, websites would just be static pages with no functionality.
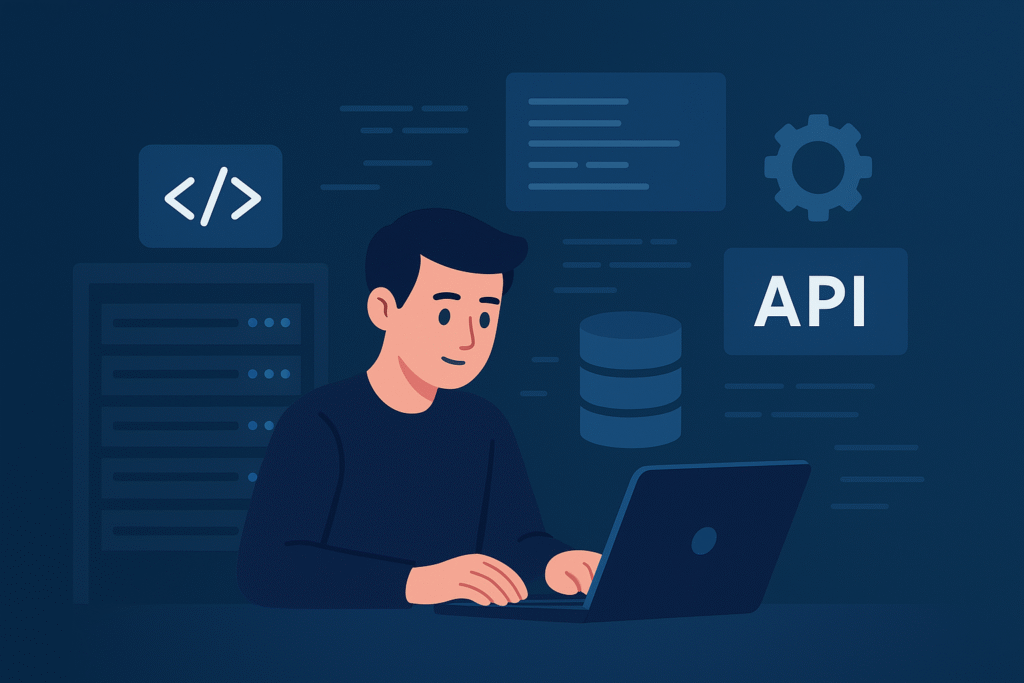
Common Back-End Technologies
- Programming Languages: Node.js (JavaScript runtime), PHP, Python, Java, and Ruby are some of the most widely used. Each has its strengths—Python for data-heavy apps, Node.js for scalable APIs, and PHP for traditional websites.
- Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB are used to store, organize, and retrieve information. For example, when you log in to a social media site, your account details are pulled from a database.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Allow the front-end to communicate with the back-end. For example, when you search for flights on a booking site, an API fetches flight details from the server and displays them on your screen.
👉 Think of the back-end as the “brain” of an application. It makes logical decisions, ensures security, and handles complex operations like payment processing or large-scale data management.
Front-End vs Back-End Development: Key Differences
| Feature | Front-End Development | Back-End Development |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Looks & user experience | Functionality & logic |
| Tools | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React | Node.js, Python, PHP, databases |
| User Interaction | Directly visible to users | Hidden from users |
| Goal | Attractive, responsive UI | Secure, fast, data-driven |
👉 The front-end vs back-end development debate isn’t about which is better—it’s about how they work together. A great website requires both: a beautiful, user-friendly interface and a powerful, reliable system behind it.
Real-World Example
To better understand the collaboration between the front-end and the back-end, let’s look at Amazon, one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms.
When you land on Amazon’s homepage, the front-end is what greets you:
- A clean layout with a search bar at the top
- Navigation menus for categories like electronics, clothing, or books
- Product images, customer reviews, star ratings, and “Add to Cart” buttons
- A personalized experience showing items based on your browsing history
All of these elements are built with modern front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They ensure that users have an engaging, responsive, and smooth shopping experience, whether they’re on a laptop, tablet, or mobile phone.
But the real magic happens behind the scenes with the back-end. For every click you make—whether it’s searching for a product, filtering by price, or checking out—complex processes are triggered. The back-end technologies handle:
- Fetching product details from massive databases in real time
- Authenticating your login and managing your account information
- Processing secure transactions when you make a purchase
- Updating inventory so that stock counts are always accurate
- Recommending products by running data algorithms
Without the front-end, users wouldn’t have a pleasant or easy way to interact with the website. Without the back-end, nothing would function—your cart wouldn’t update, payments wouldn’t process, and products wouldn’t be delivered.
This example shows how front-end vs back-end development is not about choosing one over the other. Instead, it’s about building harmony between design and functionality. Together, they create a seamless digital journey that keeps customers engaged and businesses successful.
Skills Required
Front-End Developer Skills
- Strong knowledge of design principles
- Mastery of HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Experience with frameworks like React or Angular
- Understanding of responsive design
Back-End Developer Skills
- Proficiency in server-side languages (Python, Java, PHP, Node.js)
- Knowledge of databases and APIs
- Problem-solving and logic-building
- Security and performance optimization
Future Scope
- Front-End Development: Demand is growing with the rise of interactive web apps, mobile-first design, and new frameworks.
- Back-End Development: Crucial for handling big data, AI integration, and cloud-based applications.
- Both will continue to evolve, making full-stack developers extremely valuable in the job market.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
- Students & Beginners: Helps choose a career path that fits your strengths.
- Businesses: Guides in hiring the right type of developer for projects.
- Tech Enthusiasts: Provides insight into how apps and websites function.
Conclusion
The difference between front-end and back-end development comes down to visibility and functionality. Front-end handles design and user interaction with modern front-end technologies, while back-end powers the server logic and databases using advanced back-end technologies.
Together, they build seamless, secure, and user-friendly digital experiences. Whether you choose to specialize in one or explore both, understanding the balance between these roles is the first step to a successful career in web development.